Introduction
As organizations embrace the cloud revolution, effective resource organization becomes a pivotal factor in ensuring efficient management, enhanced security, and streamlined resource allocation within the Google Cloud environment. As a professional Google Cloud architect, I understand the significance of selecting the right organization hierarchy. In this blog, we will explore various resource organization alternatives and reveal the recommended strategy for an accountability-based hierarchy that aligns with Kyndryl’s perspective.
Understanding Resource Organization on Google Cloud
Resource organization involves structuring and categorizing resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking components in a logical and hierarchical manner. By adopting a well-designed hierarchy, we can achieve enhanced governance, security, and resource optimization within the Google Cloud environment.
Alternative Approaches to Resource Organization
-
Flat Organization The flat organization offers simplicity with a single-level structure. However, it lacks scalability and fine-grained access control, making it unsuitable for large enterprises with complex resource requirements.
-
Accountability Hierarchy In my view, an accountability-based hierarchy offers the ideal solution. By creating dedicated folders or projects for each service, we ensure clear ownership, autonomy, and decentralized resource management. This approach empowers teams with autonomy to tailor configurations to their specific needs while strengthening security with fine-grained IAM controls.
-
Project-Based Hierarchy This alternative structures resources based on individual projects, which may lead to fragmentation and limited sharing of common services.
-
Environment-Based Hierarchy With environment-based organization, resources are segregated based on different environments, such as development, testing, and production. While this approach ensures segregation, it might lack the flexibility to accommodate unique project requirements.
-
Geographical Hierarchy Resources can be categorized by location, which offers regional segregation but may lead to duplication and complexity in managing global services.
-
Service-Based Hierarchy Service-based organization categorizes resources based on specific services, allowing for specialized management. However, it might not be suitable for organizations with diverse service portfolios.
-
Hybrid Hierarchy A hybrid approach combines elements from different hierarchy types to tailor the organization structure based on specific business needs. While it offers flexibility, careful planning is necessary to avoid complexity and overhead.
My recommendation is on adopting Option 2, , an accountability-based organization hierarchy with a single organization node and folders for common services at various levels within the hierarchy.
The below digram depects Accountability Hierarchy
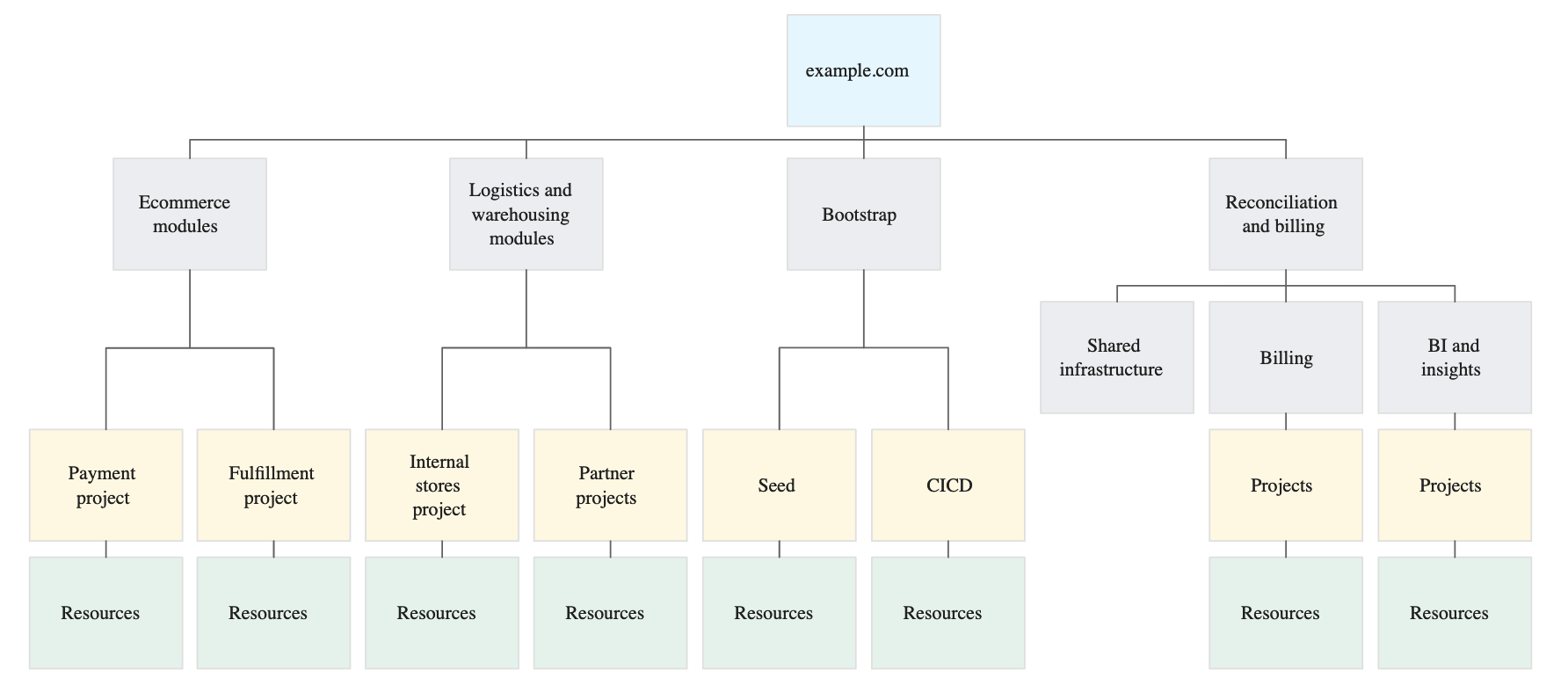
The preceding diagram illustrates a well-defined hierarchy structure for resource organization on Google Cloud. Let’s delve into the details of each level:
First Level Folders:
- e-commerce Modules and Logistics and Warehousing Modules: These folders represent specific modules within the platform offering, each requiring the same access permissions and policies throughout the product lifecycle. This approach ensures clear ownership and streamlined management for these modules.
- Reconciliation and Billing: This folder represents the product teams responsible for the end-to-end modules within specific business components of the platform offering. It promotes accountability and autonomy for these teams to manage their modules effectively.
- Bootstrap: The Bootstrap folder houses common resources required to deploy your Google Cloud infrastructure. It serves as a centralized hub for shared services and resources, enabling efficient resource utilization and cost optimization.
Within Each Folder:
Within each folder, multiple projects exist, each containing independent modules managed by different product teams. This further enhances resource segregation, ensuring each team has the freedom to tailor configurations to their specific needs.
By incorporating this well-structured hierarchy, your organization can achieve enhanced accountability, security, and resource optimization within the Google Cloud environment. It aligns perfectly with the recommended accountability-based organization hierarchy, providing clear ownership, flexibility, and improved resource management for a successful Google Cloud Landing Zone.
Key Benefits of the Accountability-Based Hierarchy:
- Improved Accountability: Clear ownership and accountability for each product or service result in better-defined roles and responsibilities.
- Flexibility and Adaptability: The organization hierarchy’s scalability and flexibility allow the Landing Zone to grow and adapt as the organization evolves. New products or services can be added without disrupting the existing structure, promoting agility.
- Enhanced Security: Implementing fine-grained IAM controls strengthens security, ensuring appropriate access controls and protecting sensitive data.
- Resource Segregation and Cost Allocation: The well-defined hierarchy facilitates resource segregation and accurate cost allocation, ensuring optimal resource utilization and cost management.
Considerations for Successful Implementation
To support this decision, we recommend implementing the following:
- Resource Naming and Tagging Guidelines: Implement standardized naming and tagging conventions for resources within each folder or project.
- IAM Policy Review and Governance: Establish a robust governance process for reviewing and managing IAM policies across folders or projects. Regular audits and updates are necessary to ensure security and compliance.
- Training and Skill Development: Provide training and skill development opportunities to teams responsible for managing resources within each folder or project.
- Resource Sharing Mechanisms: Define mechanisms and guidelines for sharing common services and resources across folders or projects.
Conclusion
Selecting the right resource organization strategy is a crucial decision for any organization embracing the cloud. As a professional Google Cloud architect, I strongly recommend adopting an accountability-based hierarchy for its improved accountability, flexibility, security, and efficient resource management. By adhering to the recommendations and considerations mentioned above, organizations can lay a strong foundation for a secure and scalable Google Cloud Landing Zone tailored to meet their specific needs and objectives.
Remember, a well-structured resource organization is the cornerstone of an effective, secure, and optimized Google Cloud infrastructure.




Leave a comment